MySQL Explain使用教程
1.Explain含义
Explain是 SQL 分析工具中非常重要的一个功能,它可以模拟优化器执行查询语句,帮助我们理解查询是如何执行的;分析查询执行计划可以帮助我们发现查询瓶颈,优化查询性能。
2.Explain作用
表的读取顺序
SQL执行时查询操作类型
可以使用哪些索引
实际使用哪些索引
每张表有多少行记录被扫描
SQL语句性能分析
3.Explain用法
数据准备
drop table orders;
drop table products;
drop table users;
CREATE TABLE users (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE products (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
price FLOAT NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_id INT NOT NULL,
order_date DATETIME NOT NULL,
total_price FLOAT NOT NULL,
product_id INT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(id),
FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
alter table users add index index_name_email (name,email);
INSERT INTO users (name, email, password)
VALUES ('张三', 'zhangsan@example.com', 'password123'),
('李四', 'lisi@example.com', 'password123'),
('王五', 'wangwu@example.com', 'password123'),
('赵六', 'zhaoli@example.com', 'password123'),
('钱七', 'qianqi@example.com', 'password123');
INSERT INTO products (name, price)
VALUES ('产品 1', 10.00),
('产品 2', 15.00),
('产品 3', 20.00),
('产品 4', 12.00),
('产品 5', 18.00);
INSERT INTO orders (user_id, order_date, total_price, product_id)
VALUES (1, '2023-02-18 10:00:00', 100.00, 1),
(2, '2023-02-18 11:00:00', 50.00, 2),
(3, '2023-02-18 12:00:00', 20.00, 3),
(4, '2023-02-18 13:00:00', 15.00, 4),
(5, '2023-02-18 14:00:00', 25.00, 5); MySQL5.7版本之前,使用Explain Partitions在Explain的基础上额外多返回partitions列;
Explain Partitions select * from users;MySQL5.7版本引入了这两个特性,直接使用Explain关键字可以将partitions列、filtered列、extra列直接查询出来。
Explain select * from users;
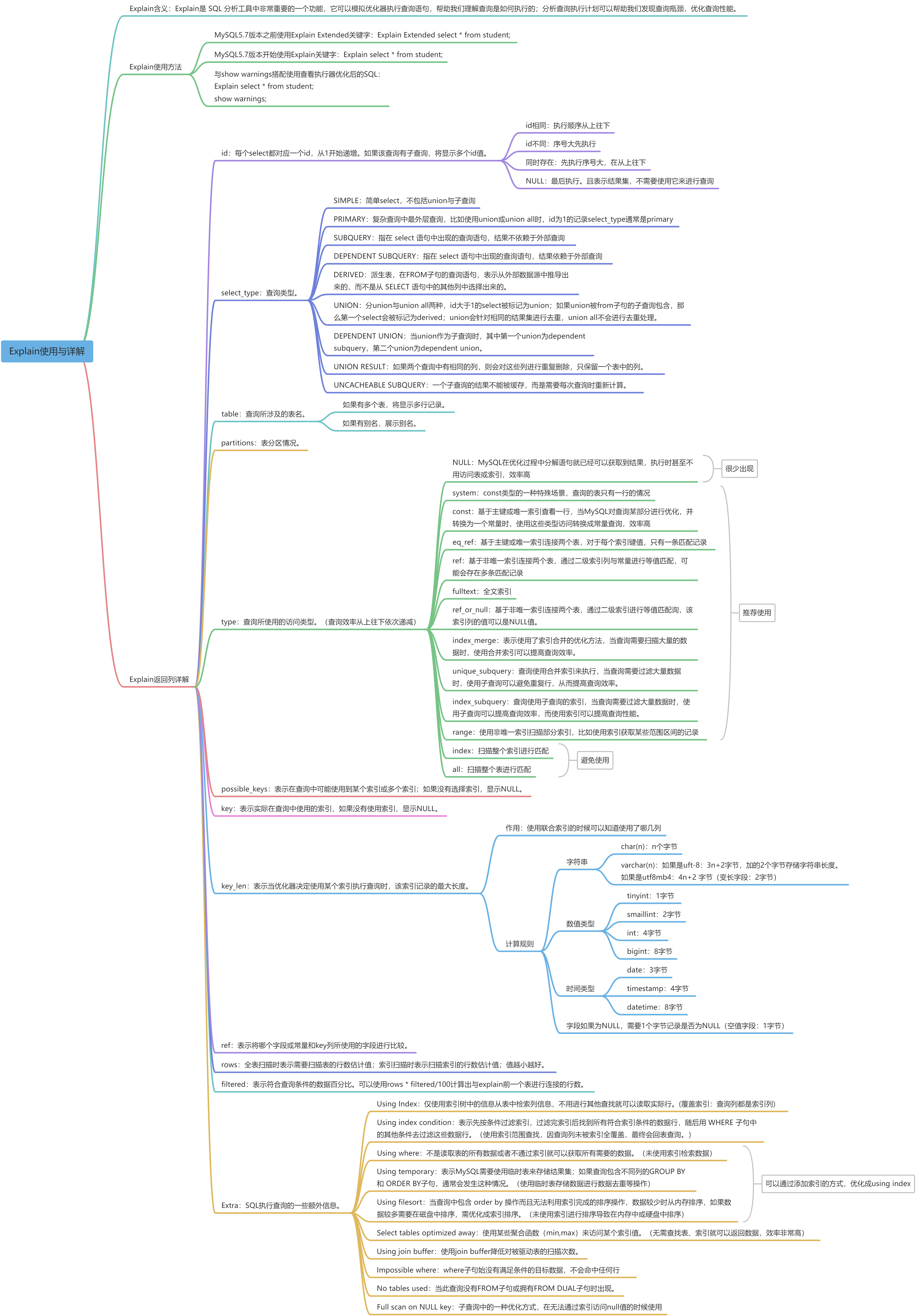
Explain语句返回列的各列含义:
这些查询列大家先留一个印象,后续会详细讲解。
4.Explain返回列详解
接下来我们将展示Explain中每个列的信息
1. id列:每个select都有一个对应的id号,并且是从1开始自增的。
●如果id序号相同,从上往下执行。
●如果id序号不同,序号大先执行。
●如果两种都存在,先执行序号大,在同级从上往下执行。
●如果显示NULL,最后执行。表示结果集,并且不需要使用它来进行查询。
id序号相同
explain
SELECT users.name, orders.total_price, products.price
FROM users
INNER JOIN orders ON users.id = orders.user_id
INNER JOIN products ON orders.product_id = products.id;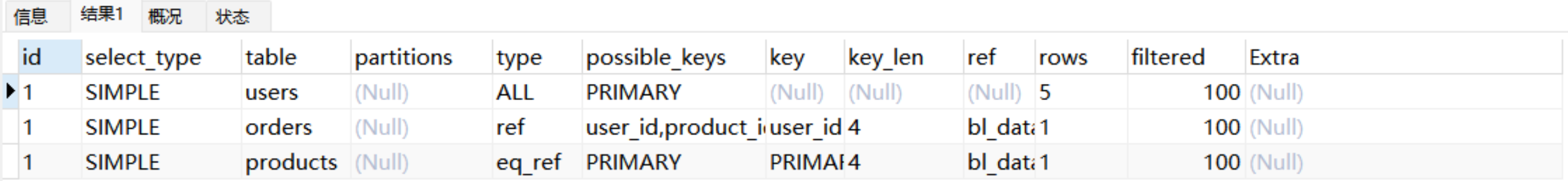
id序号不同
explain
select * from orders where product_id = (select id from products where products.price = 10);
两种都存在
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; #关闭MySQL5.7对衍生表合并优化
explain
select orders.*
from (select id from products) as temp inner join orders on temp.id = orders.product_id;
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; #还原配置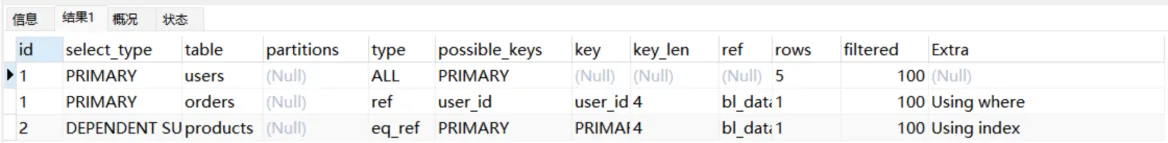
显示NULL
explain
select id from users
union
select id from products;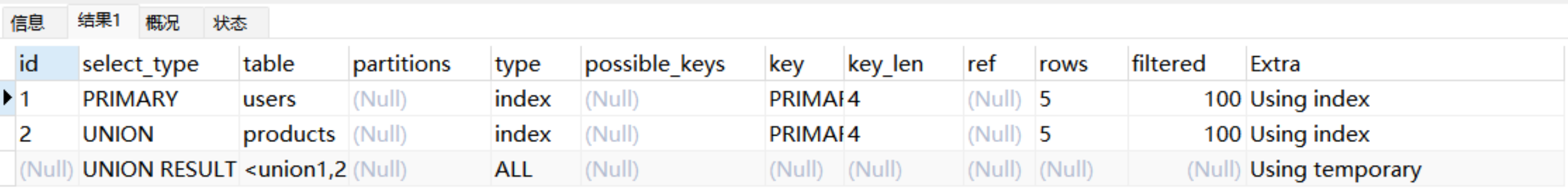
优化器会针对子查询进行一定的优化重写SQL:
EXPLAIN select * from users WHERE id in (select user_id from orders where id = 1);
show WARNINGS;2.select_type列:表示查询语句执行的查询操作类型
2.1.simple:简单select,不包括union与子查询
Explain select * from users;
连接查询
Explain select * from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.user_id;
2.2.primary:复杂查询中最外层查询,比如使用union或union all时,id为1的记录select_type通常是primary
explain
select id from users
union
select id from products;
2.3.subquery:指在 select 语句中出现的子查询语句,结果不依赖于外部查询(不在from语句中)
explain
select orders.*,(select name from products where id = 1) from orders;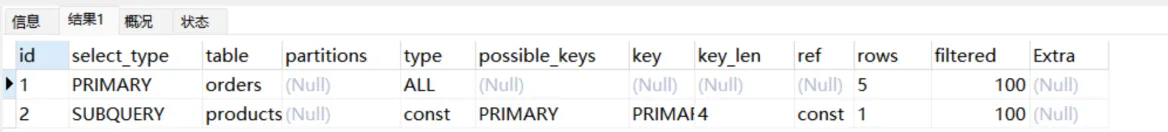
2.4.dependent subquery:指在 select 语句中出现的查询语句,结果依赖于外部查询
explain
select orders.*,(select name from products where products.id = orders.user_id) from orders;
2.5.derived:派生表,在FROM子句的查询语句,表示从外部数据源中推导出来的,而不是从 SELECT 语句中的其他列中选择出来的。
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; #关闭MySQL5.7对衍生表合并优化
explain
select * from (select user_id from orders where id = 1) as temp;
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; #还原配置
2.6.union:分union与union all两种,若第二个select出现在union之后,则被标记为union;如果union被from子句的子查询包含,那么第一个select会被标记为derived;union会针对相同的结果集进行去重,union all不会进行去重处理。
explain
select * from (
select id from products where price = 10
union
select id from orders where user_id in (1,2)
union
select id from users where name = '张三' ) as temp;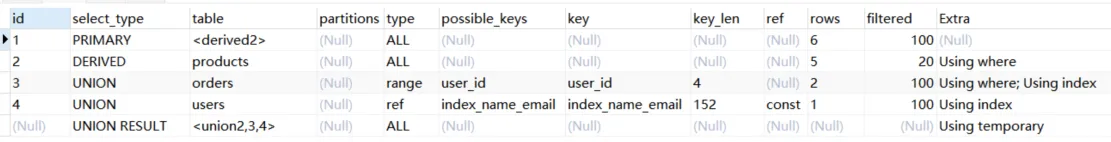
union all
explain
select * from (
select id from products where price = 10
union all
select id from orders where user_id in (1,2)
union all
select id from users where name = '张三' ) as temp;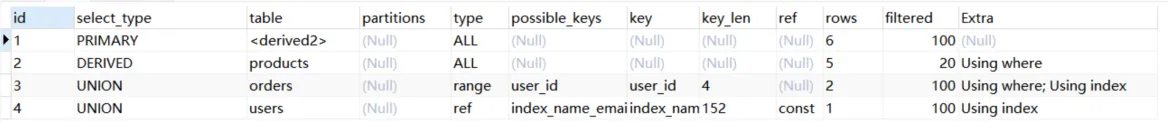
2.7.dependent union:当union作为子查询时,其中第一个union为dependent subquery,第二个union为dependent union。
explain
select * from orders where id in (
select id from products where price = 10
union
select id from orders where user_id = 2
union
select id from users where name = '张三' );
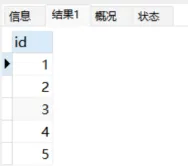
2.8.union result:如果两个查询中有相同的列,则会对这些列进行重复删除,只保留一个表中的列。
explain
select id from users
union
select id from products;
3.table列:查询所涉及的表名。如果有多个表,将显示多行记录
4.partitions列:表分区情况
查询语句所涉及的表的分区情况。具体来说,它会显示出查询语句在哪些分区上执行,以及是否使用了分区裁剪等信息。如果没有分区,该项为NULL。
5.type列:查询所使用的访问类型
效率从高到低分别为:
system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > range > index > ALL,一般来说保证range级别,最好能达到ref级别。
5.1.system:const类型的一种特殊场景,查询的表只有一行记录的情况,并且该表使用的存储引擎的统计数据是精确的
InnoDb存储引擎的统计数据不是精确的,虽然只有一条数据但是type类型为ALL;
DROP TABLE t;
CREATE TABLE t(i INT) ENGINE=InnoDb;
INSERT INTO t VALUES(1);
explain select * from t;
Memory存储引擎的统计数据是精确的,所以当只有一条记录的时候type类型为system。
DROP TABLE tt;
CREATE TABLE tt(i INT) ENGINE=memory;
INSERT INTO tt VALUES(1);
explain select * from tt;
5.2.const:基于主键或唯一索引查看一行,当MySQL对查询某部分进行优化,并转换为一个常量时,使用这些类型访问转换成常量查询,效率高
explain
select * from orders where id = 1;
5.3.eq_ref:基于主键或唯一索引连接两个表,对于每个索引键值,只有一条匹配记录,被驱动表的类型为'eq_ref'
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.id;
5.4.ref:基于非唯一索引连接两个表或通过二级索引列与常量进行等值匹配,可能会存在多条匹配记录
1.关联查询,使用非唯一索引进行匹配。
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.user_id;
2.简单查询,使用二级索引列匹配。
explain
select * from orders where user_id = 1;
5.5.range:使用非唯一索引扫描部分索引,比如使用索引获取某些范围区间的记录
explain
select * from orders where user_id > 3;
5.6.index:扫描整个索引就能拿到结果,一般是二级索引,这种查询一般为使用覆盖索引(需优化,缩小数据范围)
explain
select user_id from orders;
5.7.all:扫描整个表进行匹配,即扫描聚簇索引树(需优化,添加索引优化)
explain
select * from users;
5.8.NULL:MySQL在优化过程中分解语句就已经可以获取到结果,执行时甚至不用访问表或索引。
explain
select min(id) from users;
6.possible_keys列:表示在查询中可能使用到某个索引或多个索引;如果没有选择索引,显示NULL
7.key列:表示在查询中实际使用的索引,如果没有使用索引,显示NULL。
8.key_len列:表示当优化器决定使用某个索引执行查询时,该索引记录的最大长度(主要使用在联合索引)
联合索引可以通过这个值算出具体使用了索引中的哪些列。
使用单例索引:
explain
select * from users where id = 1;
使用联合索引:
explain
select * from users where name = '张三' and email = 'zhangsan@example.com';
计算规则:
字符串:
char(n):n个字节
varchar(n):如果是uft-8:3n+2字节,加的2个字节存储字符串长度。如果是utf8mb4:4n+2字节。
数值类型:
tinyint:1字节
smaillint:2字节
int:4字节
bigint:8字节
时间类型:
date:3字节
timestamp:4字节
datetime:8字节
字段如果为NULL,需要1个字节记录是否为NULL
9.ref列:表示将哪个字段或常量和key列所使用的字段进行比较。
当使用索引列等值查询时,与索引列进行等值匹配的对象信息。
1.常量:
explain
select * from users where name = '张三' and email = 'zhangsan@example.com';
2.字段:
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.id;
3.函数
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = trim(orders.id);
10.rows列:全表扫描时表示需要扫描表的行数估计值;索引扫描时表示扫描索引的行数估计值;值越小越好(不是结果集中的行数)
1.全表扫描
explain
select * from orders where user_id >= 3 and total_price = 25;
2.索引扫描
explain
select * from orders where user_id > 3;
11.filtered列:表示符合查询条件的数据百分比。可以使用rows * filtered/100计算出与explain前一个表进行连接的行数。
前一个表指 explain 中的id值比当前表id值小的表,id相同的时候指后执行的表。
explain
select users.* from users inner join orders on users.id = orders.id;
12.Extra列:SQL执行查询的一些额外信息
12.1.Using Index:使用非主键索引树就可以查询所需要的数据。一般是覆盖索引,即查询列都包含在辅助索引树叶子节点中,不需要回表查询。
explain
select user_id,id from orders where user_id = 1;
12.2.Using where:不通过索引查询所需要的数据
explain
select * from orders where total_price = 100;
explain
select * from orders where user_id = 1 and total_price = 100;
12.3.Using index condition:表示查询列不被索引覆盖,where 条件中是一个索引范围查找,过滤完索引后回表找到所有符合条件的数据行。
explain
select * from orders where user_id > 3;
12.4.Using temporary:表示需要使用临时表来处理查询;
1.total_price列无索引,需要创建一张临时表进行去重
explain
select distinct total_price from orders;
2.name列有联合索引
explain
select distinct name from users;
12.5.Using filesort:当查询中包含 order by 操作而且无法利用索引完成的排序操作,数据较少时从内存排序,如果数据较多需要在磁盘中排序。 需优化成索引排序。
1.total_price列无索引,无法通过索引进行排序。需要先保存total_price与对应的主键id,然后在排序total_price查找数据。
explain
select total_price from orders order by total_price;
2.name列有索引,因索引已经是排好序的所以直接读取就可以了。
explain
select name from users order by name;
12.6.Select tables optimized away:使用某些聚合函数(min,max)来访问某个索引值。
explain
select min(id) from users;
explain
select min(password) from users;
5. 总结
正确合理使用 MySQL explain 可以帮助我们更好地理解查询执行计划,并确定如何最好地优化查询SQL,提升SQL性能,增加系统稳定性。
